Syatem Dynamics:
System Dynamics is a method, that permits the analyst to decompose a complex social or behavioral system into its constituent components and then integrate them into a whole that can be easily visualized and simulated. It offers a new perspective of thinking or what is known as system thinking which is the opposite to the analysis which reduces the problem to its parts, as it deals with the problem as a whole, its parts, its relationship and its interactions with the purpose of understanding its behavior and causes. Also, with the wide spread of computers and electronic data processing systems there is a growing use of this thinking methodology as it employs computer technologies to build complex models of relationships and behavior to allow prediction of problems or situations future behavior with its changes.
System Dynamics basics:
SD is a quantitative dynamic simulation methodology used in hard (physical) and soft (social activity) systems to examine its behavioral changes over time. The method considers the holistic view of the system through its interacting feedback loops. System here is built and simulated through the cause and effect of its feedback information flow. At each instant of time, representation of the current state of the system components variables is achieved through the accumulation of events transmitted through its information flow making it an initial state for a new change. With each time step systems variables change its status as an effect of previous cause which produces new cause for another change. These feedback interactions produce a nonlinear behavior on the long term as a result of all interacting components of the system within its boundary. With this view, system status is described by accumulation of its variable (integration to become a level and called a stock) produced from a rate of change (or simply rate and called flow). As the system has always a goal, the discrepancy in the system state is the difference between the system goal and its observed status which needs an action to be introduced (a management decision). This system arrangement represents a closed feedback loop and the changing variables as traced at each instant of time give the dynamic behavior resulting from all of the system parts.
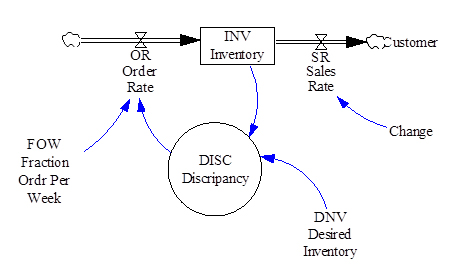
The figure gives a simplified example of the system store. Where the stored balance represents the difference between the accumulation of exchange rate and the rate of addition.Tthe system tries to adjust the difference between the goal and the current stock.
In the most general case the originator of the methodology described this system hierarchy as follows
- A. Closed boundary
- 1. Feedback loops
- (1) Goal
- (2) Observed condition
- (3) Discrepancy
- (4) Desired action
Information and Dynamic Simulation:
The way the dynamics of the system designed to represent the behavior of the system as a whole by turning the flow of information to the causal loops each episode of which has to do with the cause or effect or reaction discards or apostate. As is clear from the previous figure This method is used four symbols are represented with the flow of information through these symbols are used with differential equations. These equations can express the physical installation of the system can also describe the policies that the institution is run by management system structure. Btaataa and structure of these equations we find that they describe the goal of the decision point, with the contrast or the difference between the current state of the system and its goal to reach it, to be determined after the procedure required to correct this difference. These equations reflect together on the system model, which is entered into the computer to be able to simulate the behavior of the system numerical manner. With this method it is possible for managers to study the reasons behind the current behavior of the system, and test the changes to be taken to change the system state, where it can be this way, different policies and experience before implementing any change in reality
This example gives a representation to the store dynamics. The figure represents a simplified simulation to the store within a larger system of production firm. This representation depends on the boundary of the system to be studied.
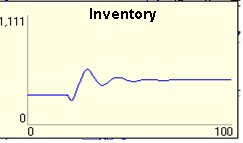
Response>
System Analysis and Design:
System analysis and design are concerned with the investigation of an organization and the design and implementation of a computerized solution to that organization needs. To analyze a system is to identify its components (devices, people, rules and procedures) and their interrelationships in order to determine its objectives, requirements, and priorities. The analyst must find ways of representing organization as a whole system, taking into consideration any economic behavioral and technical constraints. To know more about systems analyst job from the internet click here. and visit the international institute of business analysis(IIBa).